Politics
A summer food program helping kids started this year, but 13 states declined the funds

[ad_1]

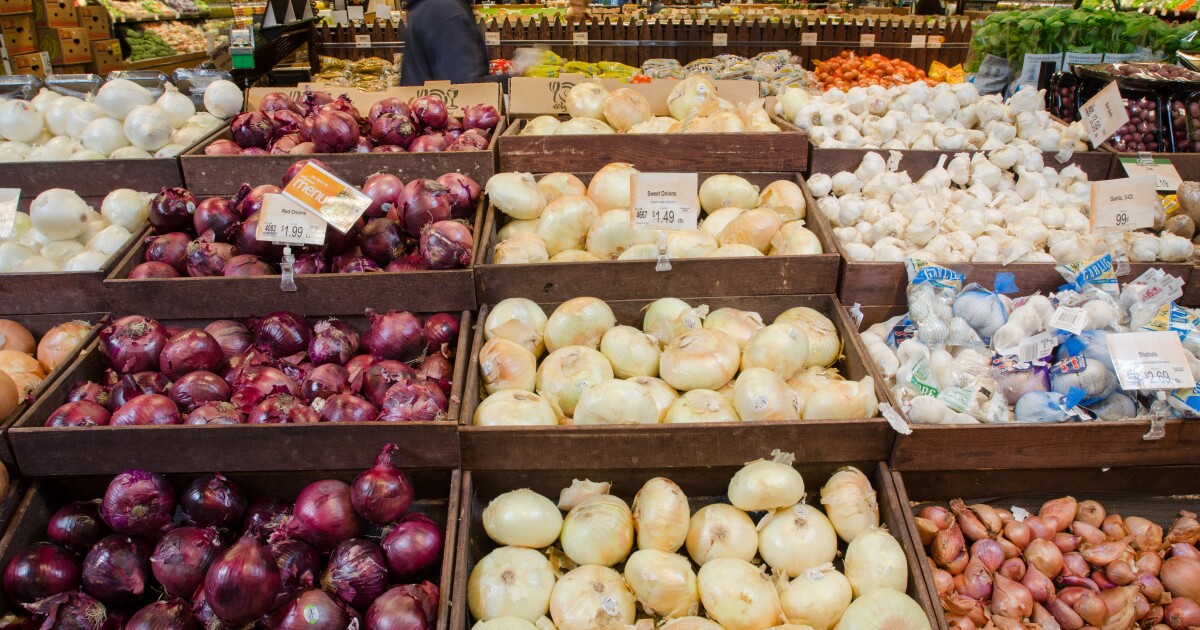
Ashton Leach’s three daughters like to eat fruit bowls and smoothies made with milk, yogurt and whatever fruit is in the house.This summer Leach and her husband know they’ll be able to afford fresh fruit, because they’re participating in the SUN Bucks program. Formally called Summer EBT, it provides $40 per child per month for groceries to eligible families over the three summer months.“So $40 doesn’t really sound like a lot. And it’s really not a lot when you break it down,” Leach said. “But that’s 40 extra dollars that you don’t have to spend.”Leach, her husband and their three young daughters live in the small town of Peggs, Oklahoma, in the Cherokee Nation. If they lived outside a tribal area, they wouldn’t have access to SUN Bucks.The program, new this year, is administered by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and expected to serve close to 21 million children with nearly $2.5 billion in grocery benefits. Yet 13 states, including Oklahoma, Iowa and South Dakota, turned down the federal funding.In Oklahoma, the Cherokee and Chickasaw Nations instead claimed the federal money and are administering the program. Cherokee Nation Principal Chief Chuck Hoskin Jr. said he found the state’s decision “bewildering.”“Once we learned that the governor rejected these dollars, it became clear that there would be an increased burden upon tribes,” Hoskin said. “But it was a burden that we were willing to bear as long as the federal resources were available.”
Anna Pope
/
Harvest Public MediaPrincipal Chief Chuck Hoskin Jr. signs papers at his desk. “It makes me proud that we are able to lead on this issue not only in Summer EBT but other issues that relate to food insecurity and food sovereignty. But it also means that we’re doing exactly what the Cherokee people have asked us to do,” Hoskin said.
The summer gapOn an average school day, about 30 million kids eat lunch at school, with some eating more than one meal. More than half of those kids are on free and reduced lunch, according to Cindy Long, the administrator of the USDA Food and Nutrition Service.“When school ends, suddenly families are faced with two or maybe even more meals a day being gone five days a week,” Long said. “Which obviously puts the kids at much greater risk of hunger, of poorer nutritional quality and frankly, puts a tremendous strain on family budgets.”For decades, the USDA has had a summer food service program, which provides meals in summer settings where kids gather together, like rec programs and summer education programs.“But it’s only historically, despite best efforts, been able to reach about 1 in 6 of the kids who receive free or reduced price school meals,” Long said.Officials knew more was needed to make up the food gap for children, and the SUN Bucks pilot project started in 2011.“It’s been shown to be very effective at reducing hunger and improving kids’ nutrition during the summer,” Long said.Families with school-age kids eligible for programs such as free and reduced lunch and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, or SNAP, qualify for SUN Bucks.The benefit cost – meaning the money going toward families – and half of the administrative cost are federally funded. States, tribal nations and territories must pay the other half of the administrative cost.Declining the fundingAlmost 13% of U.S. households were food insecure at some point in 2022, according to the USDA.Of the 13 states declining to participate in the program, five of them — Texas, Oklahoma, Mississippi, Alabama and South Carolina — are in the top 10 hungriest states in the U.S., according to Feed the Children. All 13 states are led by Republican governors.Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt’s office told media outlets in January that the state opted out of the program because of uncertainty on how the program will be administered.“It’s not reasonable to think that kids are going to go hungry in the state of Oklahoma this summer because we’re not opting into a brand-new Biden administration federal program,” Stitt told the nonprofit news outlet Oklahoma Voice.In a recent email, a spokesperson for the governor’s office said the Oklahoma Department of Human Services didn’t have enough information about program costs before the Jan. 1 deadline to submit a letter of intent. The spokesperson also said Oklahoma spends roughly $2 billion on food distribution across the state.
In Iowa, Gov. Kim Reynolds said in a press release that the Iowa Department of Health and Human Services and the Iowa Department of Education have existing programs that work with community-based providers and schools who know the needs of their community.“Federal COVID-era cash benefit programs are not sustainable and don’t provide long-term solutions for the issues impacting children and families,” Reynolds said in the press release. “An EBT card does nothing to promote nutrition at a time when childhood obesity has become an epidemic.”In Nebraska, Republican Gov. Jim Pillen at first declined the federal dollars and reiterated the decision in December.“The on-site aspect of SFSB (USDA’s Summer Food Services Program) also allows providers to spot more serious issues like malnutrition, neglect and abuse – which are often missed when children are out of school during the summer months,” Pillen said in a press release.But ultimately, the state ended up accepting the funds. Pillen announced the “Nebraska Solution.” A spokesperson for Pillen’s office said the Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services said it allows the state to accept the SUN Bucks funding and ensure the needs of children and families are met.Kelsey Boone, a senior analyst at the Food Research and Action Center, said if all states and territories participated in the program, almost 10 million more children would have been reached this summer. But she said there were some legitimate reasons for states to opt out.“We also know that there were a lot of barriers for some states to participate, including that 50% administrative match that is required for the Summer EBT program, as well as things such as resource constraints, and a projected level of effort needed to implement the program,” Boone said.She said her organization is excited to see the 37 states take part in the program and hopes to see the whole nation on board next year.“I can’t reiterate enough how much the politics of this program have been blown out of proportion and it’s not a political issue,” Boone said. “Children are hungry. They need to eat. This program provides them a way to eat.”
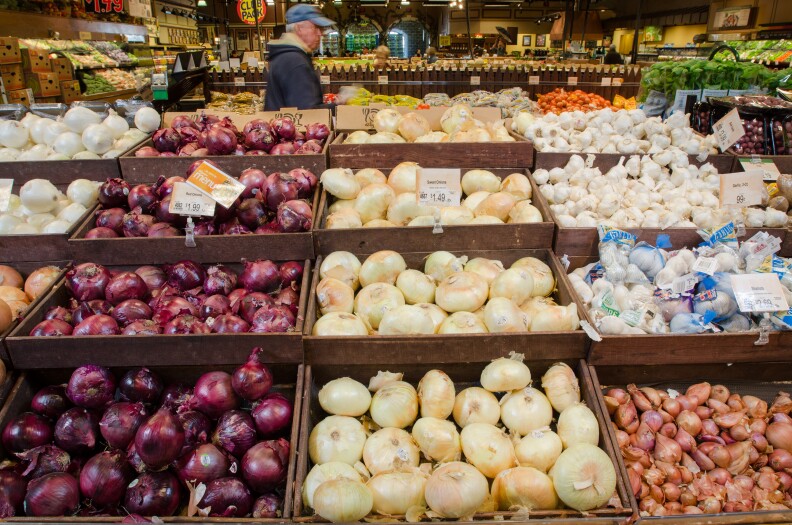
Anna Pope
/
Harvest Public MediaCherokee Nation Principal Chief Chuck Hoskin Jr. said the SUN Bucks program is appealing, because it gives people a degree of choice, the money is spent locally, and it provides support to people who need it.
Opting inFor some of the states that did opt in, there have been delays in funding.For instance, in Connecticut officials planned to roll out the program in June, but the payments are delayed. Families in Arkansas and Kansas are expected to get payments starting in July. Officials in several states say standing up a new program can take time.In Missouri, families may not get the summer payments until fall, because funding for the program wasn’t approved until May.Still, advocates are glad to be getting the program.“So ultimately, I’m hopeful that we can work out all the kinks now, that we can get a system in place,” said Christine Woody, food security policy manager at nonprofit advocacy organization Empower Missouri.She said Missouri is ranked 10th in the nation for hunger.Woody said a lot of places where meals are served are not accessible to rural communities, so a direct benefit like SUN Bucks helps. While Missouri has large urban cores, much of the state is rural.“I think a lot of the challenge with the communication on the idea of food insecurity, I think a lot of people are under the misconception that it’s an urban problem, right?” Woody said.Although rural areas make up less than two-thirds of counties in the nation, nine out of 10 counties with the highest food insecurity rates are rural, according to Feeding America.In Oklahoma, Chief Hoskin sees the need.The Cherokee Nation took part in the SUN Bucks pilot program with the USDA. He said last year, the Nation had 13,000 people in the program. As of late May of this year, Hoskin said roughly 53,000 people are enrolled in the program through the Cherokee NationFor him, food access for families plays a key role for the tribal nation to reach its health, education and economic goals.“It’s very important in any timeframe or context,” Hoskin said. “Because low-income children who need additional support for nutrition ought to get it. It’s in the national interest for them to get it, whether that is the Cherokee national interest or the United States national interest.”This story was produced in partnership with Harvest Public Media, a collaboration of public media newsrooms in the Midwest. It reports on food systems, agriculture and rural issues.
[ad_2]
Source link
Politics
Poll: Support for Missouri abortion rights amendment growing

[ad_1]

A proposed constitutional amendment legalizing abortion in Missouri received support from more than half of respondents in a new poll from St. Louis University and YouGov.That’s a boost from a poll earlier this year, which could mean what’s known as Amendment 3 is in a solid position to pass in November.SLU/YouGov’s poll of 900 likely Missouri voters from Aug. 8-16 found that 52% of respondents would vote for Amendment 3, which would place constitutional protections for abortion up to fetal viability. Thirty-four percent would vote against the measure, while 14% aren’t sure.By comparison, the SLU/YouGov poll from February found that 44% of voters would back the abortion legalization amendment.St. Louis University political science professor Steven Rogers said 32% of Republicans and 53% of independents would vote for the amendment. That’s in addition to nearly 80% of Democratic respondents who would approve the measure. In the previous poll, 24% of Republicans supported the amendment.Rogers noted that neither Amendment 3 nor a separate ballot item raising the state’s minimum wage is helping Democratic candidates. GOP contenders for U.S. Senate, governor, lieutenant governor, treasurer and secretary of state all hold comfortable leads.“We are seeing this kind of crossover voting, a little bit, where there are voters who are basically saying, ‘I am going to the polls and I’m going to support a Republican candidate, but I’m also going to go to the polls and then I’m also going to try to expand abortion access and then raise the minimum wage,’” Rogers said.Republican gubernatorial nominee Mike Kehoe has a 51%-41% lead over Democrat Crystal Quade. And U.S. Sen. Josh Hawley is leading Democrat Lucas Kunce by 53% to 42%. Some GOP candidates for attorney general, secretary of state and treasurer have even larger leads over their Democratic rivals.
Brian Munoz
/
St. Louis Public RadioHundreds of demonstrators pack into a parking lot at Planned Parenthood of St. Louis and Southwest Missouri on June 24, 2022, during a demonstration following the Supreme Court’s reversal of a case that guaranteed the constitutional right to an abortion.
One of the biggest challenges for foes of Amendment 3 could be financial.Typically, Missouri ballot initiatives with well-funded and well-organized campaigns have a better chance of passing — especially if the opposition is underfunded and disorganized. Since the end of July, the campaign committee formed to pass Amendment 3 received more than $3 million in donations of $5,000 or more.That money could be used for television advertisements to improve the proposal’s standing further, Rogers said, as well as point out that Missouri’s current abortion ban doesn’t allow the procedure in the case of rape or incest.“Meanwhile, the anti side won’t have those resources to kind of try to make that counter argument as strongly, and they don’t have public opinion as strongly on their side,” Rogers said.There is precedent of a well-funded initiative almost failing due to opposition from socially conservative voters.In 2006, a measure providing constitutional protections for embryonic stem cell research nearly failed — even though a campaign committee aimed at passing it had a commanding financial advantage.Former state Sen. Bob Onder was part of the opposition campaign to that measure. He said earlier this month it is possible to create a similar dynamic in 2024 against Amendment 3, if social conservatives who oppose abortion rights can band together.“This is not about reproductive rights or care for miscarriages or IVF or anything else,” said Onder, the GOP nominee for Missouri’s 3rd Congressional District seat. “Missourians will learn that out-of-state special interests and dark money from out of state is lying to them and they will reject this amendment.”Quade said earlier this month that Missourians of all political ideologies are ready to roll back the state’s abortion ban.“Regardless of political party, we hear from folks who are tired of politicians being in their doctor’s offices,” Quade said. “They want politicians to mind their own business. So this is going to excite folks all across the political spectrum.”
[ad_2]
Source link
Politics
Democrat Mark Osmack makes his case for Missouri treasurer

[ad_1]

Mark Osmack has been out of the electoral fray for awhile, but he never completely abandoned his passion for Missouri politics.Osmack, a Valley Park native and U.S. Army veteran, previously ran for Missouri’s 2nd Congressional District seat and for state Senate. Now he’s the Democratic nominee for state treasurer after receiving a phone call from Missouri Democratic Party Chairman Russ Carnahan asking him to run.“There’s a lot of decision making and processing and evaluation that goes into it, which is something I am very passionate and interested in,” Osmack said this week on an episode of Politically Speaking.Osmack is squaring off against state Treasurer Vivek Malek, who was able to easily win a crowded GOP primary against several veteran lawmakers including House Budget Chairman Cody Smith and state Sen. Andrew Koenig.While Malek was able to attract big donations to his political action committee and pour his own money into the campaign, Osmack isn’t worried that he won’t be able to compete in November. Since Malek was appointed to his post, Osmack contends he hasn’t proven that he’s a formidable opponent in a general election.“His actions and his decision making so far in his roughly two year tenure in that office have been questionable,” Osmack said.Among other things, Osmack was critical of Malek for placing unclaimed property notices on video gaming machines which are usually found in gas stations or convenience stores. The legality of the machines has been questioned for some time.As Malek explained on his own episode of Politically Speaking, he wanted to make sure the unclaimed property program was as widely advertised as possible. But he acknowledged it was a mistake to put the decals close to the machines and ultimately decided to remove them.Osmack said: “This doesn’t even pass the common sense sniff test of, ‘Hey, should I put state stickers claiming you might have a billion dollars on a gambling machine that is not registered with the state of Missouri?’ If we’re gonna give kudos for him acknowledging the wrong thing, it never should have been done in the first place.”Osmack’s platform includes supporting programs providing school meals using Missouri agriculture products and making child care more accessible for the working class.He said the fact that Missouri has such a large surplus shows that it’s possible to create programs to make child care within reach for parents.“It is quite audacious for [Republicans] to brag about $8 billion, with a B, dollars in state surplus, while we offer next to no social services to include pre-K, daycare, or child care,” Osmack said.Here’s are some other topics Osmack discussed on the show:How he would handle managing the state’s pension systems and approving low-income housing tax credits. The state treasurer’s office is on boards overseeing both of those programs.Malek’s decision to cut off investments from Chinese companies. Osmack said that Missouri needs to be cautious about abandoning China as a business partner, especially since they’re a major consumer of the state’s agriculture products. “There’s a way to make this work where we are not supporting communist nations to the detriment of the United States or our allies, while also maintaining strong economic ties that benefit Missouri farmers,” he said.What it was like to witness the skirmish at the Missouri State Fair between U.S. Sen. Josh Hawley and Democratic challenger Lucas Kunce.Whether Kunce can get the support of influential groups like the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee, which often channels money and staff to states with competitive Senate elections.
[ad_2]
Source link
Politics
As Illinois receives praise for its cannabis equity efforts, stakeholders work on system’s flaws

[ad_1]

Medical marijuana patients can now purchase cannabis grown by small businesses as part of their allotment, Illinois’ top cannabis regulator said, but smaller, newly licensed cannabis growers are still seeking greater access to the state’s medical marijuana customers.Illinois legalized medicinal marijuana beginning in 2014, then legalized it for recreational use in 2020. While the 2020 law legalized cannabis use for any adult age 21 or older, it did not expand licensing for medical dispensaries.Patients can purchase marijuana as part of the medical cannabis program at dual-purpose dispensaries, which are licensed to serve both medical and recreational customers. But dual-purpose dispensaries are greatly outnumbered by dispensaries only licensed to sell recreationally, and there are no medical-only dispensaries in the state.As another part of the adult-use legalization law, lawmakers created a “craft grow” license category that was designed to give more opportunities to Illinoisans hoping to legally grow and sell marijuana. The smaller-scale grow operations were part of the 2020 law’s efforts to diversify the cannabis industry in Illinois.Prior to that, all cultivation centers in Illinois were large-scale operations dominated by large multi-state operators. The existing cultivators, mostly in operation since 2014, were allowed to grow recreational cannabis beginning in 2019.Until recently, dual-purpose dispensaries have been unsure as to whether craft-grown products, made by social equity licensees — those who have lived in a disproportionately impacted area or have been historically impacted by the war on drugs — can be sold medicinally as part of a patient’s medical allotment.Erin Johnson, the state’s cannabis regulation oversight officer, told Capitol News Illinois last month that her office has “been telling dispensaries, as they have been asking us” they can now sell craft-grown products to medical patients.“There was just a track and trace issue on our end, but never anything statutorily,” she said.
Dilpreet Raju
/
Capitol News IllinoisThe graphic shows how cannabis grown in Illinois gets from cultivation centers to customers.
No notice has been posted, but Johnson’s verbal guidance comes almost two years after the first craft grow business went online in Illinois.It allows roughly 150,000 medical patients, who dispensary owners say are the most consistent purchasers of marijuana, to buy products made by social equity businesses without paying recreational taxes. However — even as more dispensaries open — the number available to medical patients has not increased since 2018, something the Cannabis Regulation Oversight Office “desperately” wants to see changed. Johnson said Illinois is a limited license state, meaning “there are caps on everything” to help control the relatively new market.Berwyn Thompkins, who operates two cannabis businesses, said the rules limited options for patients and small businesses.“It’s about access,” Thompkins said. “Why wouldn’t we want all the patients — which the (adult-use) program was initially built around — why wouldn’t we want them to have access? They should have access to any dispensary.”Customers with a medical marijuana card pay a 1% tax on all marijuana products, whereas recreational customers pay retail taxes between roughly 20 and 40% on a given cannabis product, when accounting for local taxes.While Illinois has received praise for its equity-focused cannabis law, including through an independent study that showed more people of color own cannabis licenses than in any other state, some industry operators say they’ve experienced many unnecessary hurdles getting their businesses up and running.The state, in fact, announced last month that it had opened its 100th social equity dispensary.But Steve Olson, purchasing manager at a pair of dispensaries (including one dual-purpose dispensary) near Rockford, said small specialty license holders have been left in the lurch since the first craft grower opened in October 2022.“You would think that this would be something they’re (the government) trying to help out these social equity companies with, but they’re putting handcuffs on them in so many different spots,” he said. “One of them being this medical thing.”Olson said he contacted state agencies, including the Department of Financial and Professional Regulation, months ago about whether craft products can be sold to medical patients at their retail tax rate, but only heard one response: “They all say it was an oversight.”This potentially hurt social equity companies because they sell wholesale to dispensaries and may have been missing out on a consistent customer base through those medical dispensaries.Olson said the state’s attempts to provide licensees with a path to a successful business over the years, such as with corrective lotteries that granted more social equity licenses, have come up short.“It’s like they almost set up the social equity thing to fail so the big guys could come in and swoop up all these licenses,” Olson said. “I hate to feel like that but, if you look at it, it’s pretty black and white.”Olson said craft companies benefit from any type of retail sale.“If we sell it to medical patients or not, it’s a matter of, ‘Are we collecting the proper taxes?’ That’s all it is,” he said.State revenue from cannabis taxes, licensing costs and other fees goes into the Cannabis Regulation Fund, which is used to fund a host of programs, including cannabis offense expungement, the general revenue fund, and the R3 campaign aiming to uplift disinvested communities.For fiscal year 2024, nearly $256 million was paid out from Cannabis Regulation Fund for related initiatives, which includes almost $89 million transferred to the state’s general revenue fund and more than $20 million distributed to local governments, according to the Illinois Department of Revenue.Medical access still limitedThe state’s 55 medical dispensaries that predate the 2020 legalization law, mostly owned by publicly traded multistate operators that had been operating in Illinois since 2014 under the state’s medical marijuana program, were automatically granted a right to licenses to sell recreationally in January 2020. That gave them a dual-purpose license that no new entrants into the market can receive under current law.Since expanding their clientele in 2020, Illinois dispensaries have sold more than $6 billion worth of cannabis products through recreational transactions alone.Nearly two-thirds of dispensaries licensed to sell to medical patients are in the northeast counties of Cook, DuPage, Kane, Lake and Will. Dual-purpose dispensaries only represent about 20 percent of the state’s dispensaries.While the state began offering recreational dispensary licenses since the adult-use legalization law passed, it has not granted a new medical dispensary license since 2018. That has allowed the established players to continue to corner the market on the state’s nearly 150,000 medical marijuana patients.But social equity licensees and advocates say there are more ways to level the playing field, including expanding access to medical sales.Johnson, who became the state’s top cannabis regulator in late 2022, expressed hope for movement during the fall veto session on House Bill 2911, which would expand medical access to all Illinois dispensaries.“We would like every single dispensary in Illinois to be able to serve medical patients,” Johnson said. “It’s something that medical patients have been asking for, for years.”Johnson said the bill would benefit patients and small businesses.“It’s something we desperately want to happen as a state system, because we want to make sure that medical patients are able to easily access what they need,” she said. “We also think it’s good for our social equity dispensaries, as they’re opening, to be able to serve medical patients.”Rep. Bob Morgan, D-Deerfield, who was the first statewide project coordinator for Illinois’ medical cannabis program prior to joining the legislature, wrote in an email to Capitol News Illinois that the state needs to be doing more for its patients.“Illinois is failing the state’s 150,000 medical cannabis patients with debilitating conditions. Too many are still denied the patient protections they deserve, including access to their medicine,” Morgan wrote, adding he would continue to work with stakeholders on further legislation.Capitol News Illinois is a nonprofit, nonpartisan news service covering state government. It is distributed to hundreds of newspapers, radio and TV stations statewide. It is funded primarily by the Illinois Press Foundation and the Robert R. McCormick Foundation, along with major contributions from the Illinois Broadcasters Foundation and Southern Illinois Editorial Association.
[ad_2]
Source link
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoPrenzler ‘reconsidered’ campaign donors, accepts vendor funds
-
Board Bills1 year ago
2024-2025 Board Bill 80 — Prohibiting Street Takeovers
-

 Board Bills3 years ago
Board Bills3 years ago2022-2023 Board Bill 168 — City’s Capital Fund
-

 Business3 years ago
Business3 years agoFields Foods to open new grocery in Pagedale in March
-

 Business3 years ago
Business3 years agoWe Live Here Auténtico! | The Hispanic Chamber | Community and Connection Central
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoOK, That New Cardinals/Nelly City Connect Collab Is Kind of Great
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoSt.Louis Man Sounds Just Like Whitley Hewsten, Plans on Performing At The Shayfitz Arena.
-

 Local News2 years ago
Local News2 years agoFox 2 Reporter Tim Ezell Reveals He Has Parkinson’s Disease | St. Louis Metro News | St. Louis