Politics
How Illinois’ hands-off approach to homeschooling leaves children at risk
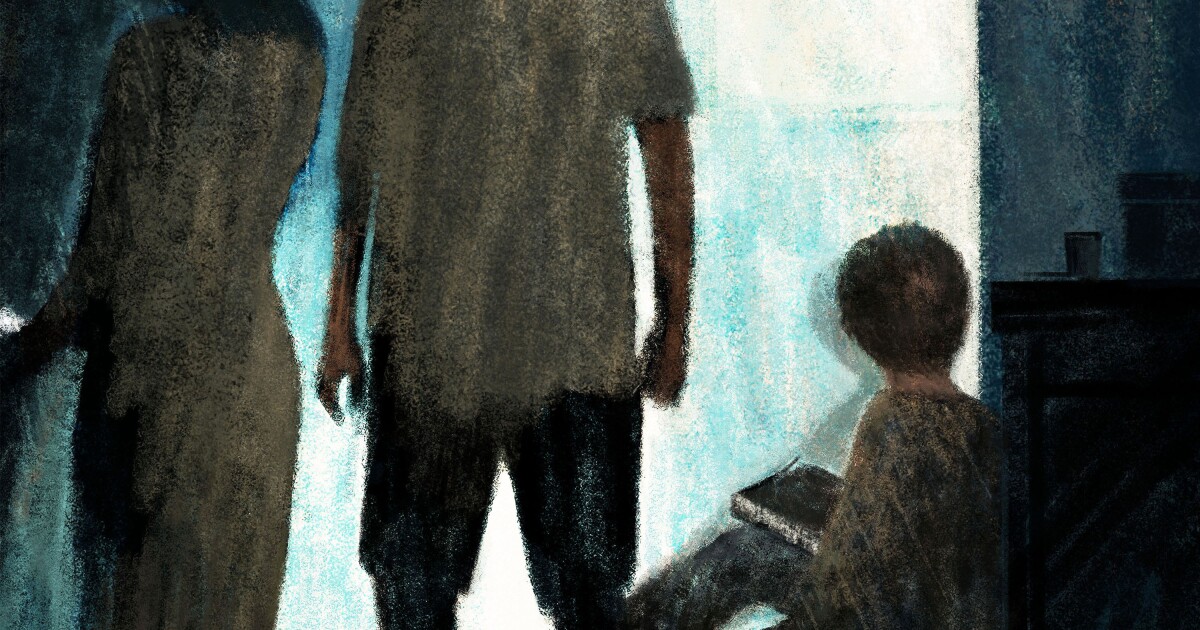
[ad_1]

This article was produced for ProPublica’s Local Reporting Network in partnership with Capitol News Illinois. Sign up for Dispatches to get stories like this one as soon as they are published.It was on L.J.’s 11th birthday, in December 2022, that child welfare workers finally took him away. They arrived at his central Illinois home to investigate an abuse allegation and decided on the spot to remove the boy along with his baby brother and sister — the “Irish twins,” as their parents called them.His mother begged to keep the children while her boyfriend told child welfare workers and the police called to the scene that they could take L.J.: “You wanna take someone? Take that little motherfucker down there or wherever the fuck he is at. I’ve been trying to get him out of here for a long time.”By that time, L.J. told authorities he hadn’t been in a classroom for years, according to police records. First came COVID-19. Then, in August 2021 when he was going to have to repeat the third grade, his mother and her boyfriend decided that L.J. would be homeschooled and that they would be his teachers. In an instant, his world shrank to the confines of a one-bedroom apartment in the small Illinois college town of Charleston — no teachers, counselors or classmates.In that apartment, L.J. would later tell police, he was beaten and denied food: Getting leftovers from the refrigerator was punishable by a whipping with a belt; sass was met with a slap in the face.L.J. told police he got no lessons or schoolwork at home. Asked if he had learned much, L.J. replied, “Not really.”
Obtained by Capitol News Illinois and ProPublica
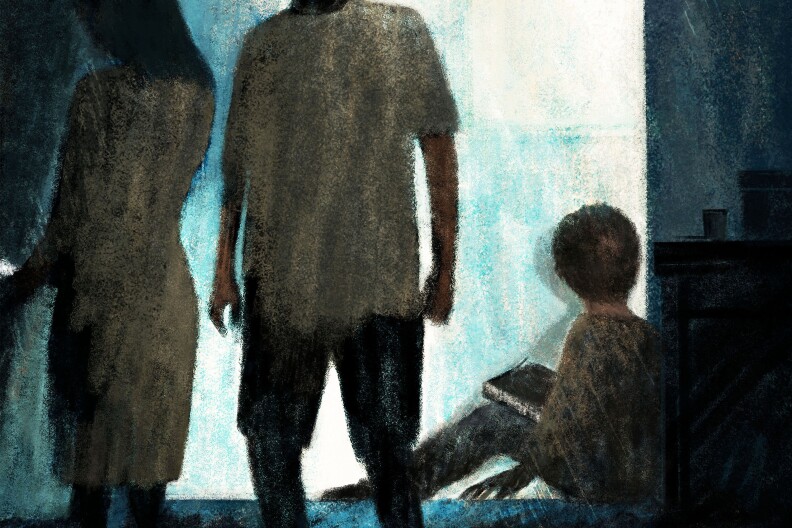
/
Highlighted and redacted by ProPublicaL.J. told police that he was sometimes left alone to care for his baby siblings and punished for eating food without permission, according to Charleston Police Department records.
Reporters are using the first and middle initials of the boy, who is now 12 and remains in state custody, to protect his identity.While each state has different regulations for homeschooling — and most of them are relatively weak — Illinois is among a small minority that places virtually no rules on parents who homeschool their children: The parents aren’t required to register with any governmental agency, and no tests are required. Under Illinois law, they must provide an education equivalent to what is offered in public schools, covering core subjects like math, language arts, science and health. But parents don’t have to have a high school diploma or GED, and state authorities cannot compel them to demonstrate their teaching methods or prove attendance, curriculum or testing outcomes.The Illinois State Board of Education said in a statement that regional education offices are empowered by Illinois law to request evidence that a family that homeschools is providing an adequate course of instruction. But, the spokesperson said, their “ability to intervene can be limited.”Educational officials say this lack of regulation allows parents to pull vulnerable children like L.J. from public schools then not provide any education for them. They call them “no schoolers.”No oversight also means children schooled at home lose the protections schools provide, including teachers, counselors, coaches and bus drivers — school personnel legally bound to report suspected child abuse and neglect. Under Illinois law, parents may homeschool even if they would be disqualified from working with youth in any other setting; this includes parents with violent criminal records or pending child abuse investigations, or those found to have abused children in the past.The number of students from preschool to 12th grade enrolled in the state’s public schools has dropped by about 127,000 since the pandemic began. Enrollment losses have outpaced declines in population, according to a report by Advance Illinois, a nonprofit education policy and advocacy organization. And, despite conventional wisdom, the drop was also not the result of wealthier families moving their children to private schools: After the pandemic, private school enrollment declined too, according to the same report.In the face of this historic exodus from public schools, Capitol News Illinois and ProPublica set out to examine the lack of oversight by education and child welfare systems when some of those children disappear into families later accused of no-schooling and, sometimes, abuse and neglect.Reporters found no centralized system for investigating homeschooling concerns. Educational officials said they were ill equipped to handle cases where parents are accused of neglecting their children’s education. They also said the state’s laws made it all but impossible to intervene in cases where parents claim they are homeschooling. Reporters also found that under the current structure, concerns about homeschooling bounce between child welfare and education authorities, with no entity fully prepared to step in.“Although we have parents that do a great job of homeschooling, we have many ‘no schoolers’” said Angie Zarvell, superintendent of a regional education office about 100 miles southwest of Chicago that covers three counties and 23 school districts. “The damage this is doing to small rural areas is great. These children will not have the basic skills needed to be contributing members of society.”Regional education offices, like the one Zarvell oversees, are required by law to identify children who are truant and try to help get them back into school.
We have many ‘no schoolers.’ The damage this is doing to small rural areas is great. These children will not have the basic skills needed to be contributing members of society.
Angie Zarvell, superintendent of a regional education office that covers 23 school districts
But once parents claim they are homeschooling, “our hands are tied,” said Superintendent Michelle Mueller, whose regional office is located about 60 miles north of St. Louis.Even the state’s child welfare agency can do little: Reports to its child abuse hotline alleging that parents are depriving their children of an education have multiplied, but the Department of Children and Family Services doesn’t investigate schooling matters. Instead, it passes reports to regional education offices.Todd Vilardo, who since 2017 has been superintendent of the school district where L.J. was enrolled, said he is seeing more and more children outside of school during the day. He wonders, “‘Aren’t they supposed to be in school?’ But I’m reminded that maybe they’re homeschooled,” said Vilardo, who has worked in the Charleston school district for 33 years. “Then I’m reminded that there are very few effective checks and balances on home schools.”A huge crack in our systemThere’s no way to determine the precise number of children who are homeschooled. In 2022, 4,493 children were recorded as withdrawn to homeschool, a number that is likely much higher because Illinois doesn’t require parents to register homeschooled children. That is a little more than double the number a decade before.In late fall of 2020, L.J. was one of the kids who slipped out of school. After a roughly five-month hiatus from the classroom during the pandemic, L.J.’s school resumed in-person classes. The third grader, however, was frequently absent.At home, tensions ran high. In the 640-square-foot apartment, L.J.’s mother, Ashley White, and her boyfriend, Brian Anderson, juggled the demands of three children including two born just about 10 months apart.White, now 31, worked at a local fast-food restaurant. Anderson, now 51, who uses a wheelchair, had applied for disability payments. Anderson doesn’t have a valid driver’s license. The family lived in a subsidized housing complex for low-income seniors and people with disabilities.In an interview with reporters in late February, 14 months after L.J. had been taken into custody by the state, the couple offered a range of explanations for why he hadn’t been in school. L.J. had been suspended and barred from returning, they said, though school records show no expulsion. They also said they had tried to put L.J. in an alternative school for children with special needs, but he didn’t have a diagnosis that qualified him to attend.The couple made clear they believed that L.J. was a problem child who could get them in trouble; they said they thought he could get them sued. In the interview, Anderson called L.J. a pathological liar, a thief and a bad kid.“I have 11 kids, never had a problem with any of them, never,” Anderson said. “I’ve never had a problem like this,” he said of L.J. The boy, he said, lacked discipline and continued to get “worse and worse and worse every year” he’d known him.To support the idea that L.J. was combative, White provided a copy of a screenshot taken from a school chat forum in which the boy cursed at his schoolmates.At the end of the school year, in spring 2021, the principal told White and Anderson that the boy would have to repeat the third grade. Rather than have L.J. held back, the couple pulled him out of school to homeschool. They didn’t have to fill out any paperwork or give a reason.On any given day in Illinois, a parent can make that same decision. That’s due to a series of court and legislative decisions that strengthened parents’ rights against state interference in how they educate their children.In 1950, the Illinois Supreme Court heard a case involving college-educated parents who kept their 7-year-old daughter at home. Those parents, Seventh-day Adventists, argued that a public school education produced a “pugnacious character” and believed the mother was the best teacher and nature was the best textbook. The judges ruled in their favor, finding that, in many respects under the law, homeschools are essentially like private schools: not required to register kids with the state and not subject to testing or curriculum mandates.In 1989, the legislature voted to change how educational neglect cases are handled. Before the vote, DCFS was allowed to investigate parents who failed to ensure their child’s education just as it does other types of neglect. In a bipartisan vote, the General Assembly changed that, in part to reduce caseloads on DCFS — which has been overburdened and inadequately staffed for decades — and also in response to concerns about state interference from families who homeschool.Since then, DCFS has referred complaints about schooling that come in to its child abuse hotline over to regional offices of education. The letter accompanying the educational neglect referral form ends with: “This notice is for your information and pursuit only. No response to this office is required.”
Obtained by Capitol News Illinois and ProPublica
/
Highlighted and redacted by ProPublicaThe Department of Children and Family Services forwards educational neglect claims made to its hotline to regional offices of education handling truancy, stating educational officials need not report findings back.
Tierney Stutz, executive deputy director at DCFS, said that regional education officials are welcome to report back findings, but that “DCFS does not have statutory authority to act on this information.”“Unfortunately, this is a huge crack in our system,” said Amber Quirk, regional superintendent of the office of education that covers densely populated DuPage County in the Chicago suburbs.To see how this system is working, reporters obtained more than 450 of these educational neglect reports, representing over a third of the more than 1,200 forwarded by DCFS over three years ending in 2023. About 10% of them specifically cited substandard homeschooling claims. But officials said that in many of the other reported cases of kids out of school, they found that families also claimed they were homeschooling.Faced with cases of truancy or educational neglect, county prosecutors can press charges against parents. But if they do, parents can lean on Illinois’ parental protections when they defend themselves in court from a truancy charge.That’s been the experience of Dirk Muffler, who oversees truancy intervention at a regional office of education covering five counties in west-central Illinois. “We’ve gone through an entire truancy process, literally standing on the courthouse steps getting ready to walk in to screen a kid into court and the parents say, ‘We are homeschooling.’ I have to just walk away then.”More recently, the ISBE made one more decision to loosen the monitoring of parents who homeschool: For years, school districts and regional offices distributed voluntary registration forms to families who homeschool, some of whom returned them. Then last year, the state agency told those regional offices that they no longer had to send those forms to ISBE.“The homeschool registration form was being misinterpreted in some instances that ISBE was reviewing or approving homeschool programs, which it does not have statutory authority to do,” an ISBE spokesperson told the news organizations.
All we want is to be left alone. And Illinois has been so good. We have probably the best state in the nation to homeschool.
Kirk Smith, executive director of Illinois Christian Home Educators
Over the years, the legislature has taken up proposals to strengthen the state’s oversight of homeschooling. In 2011, lawmakers considered requiring parents to notify their local school districts of their intent to homeschool, and in 2019 they considered calling for DCFS to inspect all homeschools and have ISBE approve their curriculum.Each time, however, the state’s strong homeschooling lobby, mostly made up of religious-based organizations, stepped in.This March, under sponsorship of the Illinois Christian Home Educators, homeschoolers massed at the state Capitol as they have for decades for Cherry Pie Day, bringing pies to each of the state’s 177 lawmakers.Kirk Smith, the organization’s executive director and former public school teacher, summed up his group’s appeal to lawmakers: “All we want is to be left alone. And Illinois has been so good. We have probably the best state in the nation to homeschool.”
Dominique Martinez-Powell
/
Saluki Local Reporting Lab, for Capitol News IllinoisFamilies who homeschool and their supporters assembled at the Illinois Capitol in March to give lawmakers cherry pies, a gesture of gratitude for maintaining regulation-free homeschooling.
“Nobody knows. He’s not in school.”Just days after child protection workers took 11-year-old L.J. into protective custody on his birthday, a 9-year-old homeschooled boy, 240 miles away, disappeared and was missing for months before police went looking for him.Though the case of Zion Staples was covered in the media, it has not been previously reported that his homeschooling status delayed the discovery of his death.Zion had been living in Rock Island, in the northwest part of the state, with his mother, Sushi Staples. The family had a long history of abuse and neglect investigations by DCFS, and Staples had lost two kids to foster care in Illinois nearly two decades before because she mistreated them; the children were not returned to her. The most recent investigation by DCFS was in 2021. The department did not find enough evidence to find mistreatment and the case was closed.Despite her past involvement with child welfare services, no Illinois laws restricted her from homeschooling the children who remained in her care, including Zion and five others who were then ages 8 to 14.When reporters asked DCFS for his schooling status, the agency’s responses revealed considerable confusion about where he was being educated. DCFS originally told the news organizations that Zion was enrolled in an online school program, but the company that DCFS said had been providing his schooling told reporters that Zion had never been enrolled. DCFS later clarified that his mother said he was leaving public school in August 2021 to attend an online program, but no one was required to verify this information.On a December morning in 2022, Staples told police she returned home from running errands and found Zion dead. A coroner would later find that he died from an accidental, self-inflicted shot fired from a gun the children found in the house. His mother hid the body and later confided to her friend, Laterrica Wilson, that she did it because she did not want to risk losing her other children.“She said: ‘Nobody knows. He’s not in school. He’s homeschooled. I’ve got this figured out,’” Wilson recalled in an interview with a reporter about a conversation she had with Staples a few months after the child had died. “She said she had too much to lose.”Wilson, who lives in Florida, said it was one of several calls she had with Staples over the course of months as she tried to figure out what had happened and what to do about it. Police records indicate that in July, in response to a call from Wilson, they visited the home. Staples denied the child even existed. Later, when police executed a search warrant, officers found Zion’s body in a metal trash can in the garage; he was still wearing his Spiderman pajama bottoms. He’d been dead for seven months, an autopsy revealed.Staples was charged with concealing a death, failure to report the death of a child within 24 hours and obstructing justice. Staples pleaded guilty to felony endangering the health of a child in February and was sentenced to two years in prison in April.Staples did not respond to a letter sent to her in prison seeking comment on this case.DCFS and its university partners study all sorts of risks to children involved with the child welfare system, but they’ve never examined homeschooling and do not track the number of children the agency comes in contact with who are homeschooled. While the agency’s inspector general is required to file reports on every child who dies in foster care or whose family the agency had investigated within the preceding year of the child’s death, the children’s schooling status is rarely noted in them.For L.J., homeschooling rules also blinded school officials to abuse he suffered, although their administrative office is within sight of his apartment complex. About five months passed from when he was withdrawn to homeschool in the summer of 2021 before the first signs of help arrived. Following a call to its hotline in January 2022, DCFS found White and Anderson neglectful, citing inadequate supervision, but that did not result in L.J. returning to school. DCFS offered services, but Anderson and White declined.DCFS received more calls to its hotline in June 2022 and again that September, alleging that Anderson and White had mistreated L.J. In both of those cases, DCFS investigators did not find enough evidence to support those allegations and closed the cases.The caller in September told DCFS the boy appeared malnourished. L.J. hadn’t been in school since 2019, the caller reported. But DCFS said they did not pursue an investigation into his schooling matters because it wasn’t in their policies to do so.It did send an educational neglect report to Kyle Thompson, the superintendent of schools overseeing the regional office of education in Charleston. The form didn’t mention physical abuse, but it did say that L.J. had begged for food from neighbors, that doctors were concerned about his weight and that a DCFS caseworker had recently visited the home but no one had answered the door.
Obtained by Capitol News Illinois and ProPublica
/
Highlighted and redacted by ProPublicaDCFS fielded a complaint about L.J. to its hotline in September 2022 that included concerns about his eating and weight; it also said he hadn’t been in school for years. The department forwarded these details on an educational neglect report to the regional office of education in Charleston.
Thompson was in his office when the educational neglect report ended up on his desk on an October afternoon. Alarmed when he read the allegations, Thompson went to the apartment that same day. White and Anderson came to the door, Thompson recalled, and eventually agreed to meet with school officials.“I really feel like we may have saved that kid’s life that day,” Thompson said.But Anderson and White continued to keep L.J. at home.In November, a grocery store manager found L.J. in the parking lot begging for quarters and called police, who took L.J. home and later issued a ticket to White and Anderson for violating a city truancy ordinance. L.J. hadn’t been to school the whole year — 70 days.Anderson said he didn’t know why he was cited, since he was homeschooling. “Apparently, it wasn’t good enough for the school system,” he told reporters.A few days later, police and child welfare services again visited the home and found welts and bruises on L.J.’s back. L.J. said Anderson had beaten him with a belt as punishment for eating leftover Salisbury steak and potatoes without permission. The boy also told child welfare workers he had not showered for two weeks.Anderson and White would later tell reporters L.J. was on a diet of fruits and vegetables because he was too fat and prediabetic, but L.J. told police he ate mostly cereal. Though DCFS found credible evidence of both neglect and abuse in its November and December investigations, the couple said they did not abuse L.J. or deny him an education. They are still trying to get the two younger children back, but they say they don’t want L.J. In an April court custody hearing, a judge in their child welfare case admonished them for not accepting responsibility for their treatment of L.J., including keeping him from school.For its part, the state did ultimately take responsibility for L.J.’s schooling: Caseworkers took the children into custody on a Friday. The following Monday, L.J. returned to public school.Have a news tip regarding homeschooling, chronic truancy or educational neglect? Email them to Molly Parker or Beth Hundsdorfer at investigations@capitolnewsillinois.com.ProPublica’s Mollie Simon contributed research and Andrew Adams of Capitol News Illinois contributed data reporting.
[ad_2]
Source link
Politics
Poll: Support for Missouri abortion rights amendment growing

[ad_1]

A proposed constitutional amendment legalizing abortion in Missouri received support from more than half of respondents in a new poll from St. Louis University and YouGov.That’s a boost from a poll earlier this year, which could mean what’s known as Amendment 3 is in a solid position to pass in November.SLU/YouGov’s poll of 900 likely Missouri voters from Aug. 8-16 found that 52% of respondents would vote for Amendment 3, which would place constitutional protections for abortion up to fetal viability. Thirty-four percent would vote against the measure, while 14% aren’t sure.By comparison, the SLU/YouGov poll from February found that 44% of voters would back the abortion legalization amendment.St. Louis University political science professor Steven Rogers said 32% of Republicans and 53% of independents would vote for the amendment. That’s in addition to nearly 80% of Democratic respondents who would approve the measure. In the previous poll, 24% of Republicans supported the amendment.Rogers noted that neither Amendment 3 nor a separate ballot item raising the state’s minimum wage is helping Democratic candidates. GOP contenders for U.S. Senate, governor, lieutenant governor, treasurer and secretary of state all hold comfortable leads.“We are seeing this kind of crossover voting, a little bit, where there are voters who are basically saying, ‘I am going to the polls and I’m going to support a Republican candidate, but I’m also going to go to the polls and then I’m also going to try to expand abortion access and then raise the minimum wage,’” Rogers said.Republican gubernatorial nominee Mike Kehoe has a 51%-41% lead over Democrat Crystal Quade. And U.S. Sen. Josh Hawley is leading Democrat Lucas Kunce by 53% to 42%. Some GOP candidates for attorney general, secretary of state and treasurer have even larger leads over their Democratic rivals.
Brian Munoz
/
St. Louis Public RadioHundreds of demonstrators pack into a parking lot at Planned Parenthood of St. Louis and Southwest Missouri on June 24, 2022, during a demonstration following the Supreme Court’s reversal of a case that guaranteed the constitutional right to an abortion.
One of the biggest challenges for foes of Amendment 3 could be financial.Typically, Missouri ballot initiatives with well-funded and well-organized campaigns have a better chance of passing — especially if the opposition is underfunded and disorganized. Since the end of July, the campaign committee formed to pass Amendment 3 received more than $3 million in donations of $5,000 or more.That money could be used for television advertisements to improve the proposal’s standing further, Rogers said, as well as point out that Missouri’s current abortion ban doesn’t allow the procedure in the case of rape or incest.“Meanwhile, the anti side won’t have those resources to kind of try to make that counter argument as strongly, and they don’t have public opinion as strongly on their side,” Rogers said.There is precedent of a well-funded initiative almost failing due to opposition from socially conservative voters.In 2006, a measure providing constitutional protections for embryonic stem cell research nearly failed — even though a campaign committee aimed at passing it had a commanding financial advantage.Former state Sen. Bob Onder was part of the opposition campaign to that measure. He said earlier this month it is possible to create a similar dynamic in 2024 against Amendment 3, if social conservatives who oppose abortion rights can band together.“This is not about reproductive rights or care for miscarriages or IVF or anything else,” said Onder, the GOP nominee for Missouri’s 3rd Congressional District seat. “Missourians will learn that out-of-state special interests and dark money from out of state is lying to them and they will reject this amendment.”Quade said earlier this month that Missourians of all political ideologies are ready to roll back the state’s abortion ban.“Regardless of political party, we hear from folks who are tired of politicians being in their doctor’s offices,” Quade said. “They want politicians to mind their own business. So this is going to excite folks all across the political spectrum.”
[ad_2]
Source link
Politics
Democrat Mark Osmack makes his case for Missouri treasurer

[ad_1]

Mark Osmack has been out of the electoral fray for awhile, but he never completely abandoned his passion for Missouri politics.Osmack, a Valley Park native and U.S. Army veteran, previously ran for Missouri’s 2nd Congressional District seat and for state Senate. Now he’s the Democratic nominee for state treasurer after receiving a phone call from Missouri Democratic Party Chairman Russ Carnahan asking him to run.“There’s a lot of decision making and processing and evaluation that goes into it, which is something I am very passionate and interested in,” Osmack said this week on an episode of Politically Speaking.Osmack is squaring off against state Treasurer Vivek Malek, who was able to easily win a crowded GOP primary against several veteran lawmakers including House Budget Chairman Cody Smith and state Sen. Andrew Koenig.While Malek was able to attract big donations to his political action committee and pour his own money into the campaign, Osmack isn’t worried that he won’t be able to compete in November. Since Malek was appointed to his post, Osmack contends he hasn’t proven that he’s a formidable opponent in a general election.“His actions and his decision making so far in his roughly two year tenure in that office have been questionable,” Osmack said.Among other things, Osmack was critical of Malek for placing unclaimed property notices on video gaming machines which are usually found in gas stations or convenience stores. The legality of the machines has been questioned for some time.As Malek explained on his own episode of Politically Speaking, he wanted to make sure the unclaimed property program was as widely advertised as possible. But he acknowledged it was a mistake to put the decals close to the machines and ultimately decided to remove them.Osmack said: “This doesn’t even pass the common sense sniff test of, ‘Hey, should I put state stickers claiming you might have a billion dollars on a gambling machine that is not registered with the state of Missouri?’ If we’re gonna give kudos for him acknowledging the wrong thing, it never should have been done in the first place.”Osmack’s platform includes supporting programs providing school meals using Missouri agriculture products and making child care more accessible for the working class.He said the fact that Missouri has such a large surplus shows that it’s possible to create programs to make child care within reach for parents.“It is quite audacious for [Republicans] to brag about $8 billion, with a B, dollars in state surplus, while we offer next to no social services to include pre-K, daycare, or child care,” Osmack said.Here’s are some other topics Osmack discussed on the show:How he would handle managing the state’s pension systems and approving low-income housing tax credits. The state treasurer’s office is on boards overseeing both of those programs.Malek’s decision to cut off investments from Chinese companies. Osmack said that Missouri needs to be cautious about abandoning China as a business partner, especially since they’re a major consumer of the state’s agriculture products. “There’s a way to make this work where we are not supporting communist nations to the detriment of the United States or our allies, while also maintaining strong economic ties that benefit Missouri farmers,” he said.What it was like to witness the skirmish at the Missouri State Fair between U.S. Sen. Josh Hawley and Democratic challenger Lucas Kunce.Whether Kunce can get the support of influential groups like the Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee, which often channels money and staff to states with competitive Senate elections.
[ad_2]
Source link
Politics
As Illinois receives praise for its cannabis equity efforts, stakeholders work on system’s flaws

[ad_1]

Medical marijuana patients can now purchase cannabis grown by small businesses as part of their allotment, Illinois’ top cannabis regulator said, but smaller, newly licensed cannabis growers are still seeking greater access to the state’s medical marijuana customers.Illinois legalized medicinal marijuana beginning in 2014, then legalized it for recreational use in 2020. While the 2020 law legalized cannabis use for any adult age 21 or older, it did not expand licensing for medical dispensaries.Patients can purchase marijuana as part of the medical cannabis program at dual-purpose dispensaries, which are licensed to serve both medical and recreational customers. But dual-purpose dispensaries are greatly outnumbered by dispensaries only licensed to sell recreationally, and there are no medical-only dispensaries in the state.As another part of the adult-use legalization law, lawmakers created a “craft grow” license category that was designed to give more opportunities to Illinoisans hoping to legally grow and sell marijuana. The smaller-scale grow operations were part of the 2020 law’s efforts to diversify the cannabis industry in Illinois.Prior to that, all cultivation centers in Illinois were large-scale operations dominated by large multi-state operators. The existing cultivators, mostly in operation since 2014, were allowed to grow recreational cannabis beginning in 2019.Until recently, dual-purpose dispensaries have been unsure as to whether craft-grown products, made by social equity licensees — those who have lived in a disproportionately impacted area or have been historically impacted by the war on drugs — can be sold medicinally as part of a patient’s medical allotment.Erin Johnson, the state’s cannabis regulation oversight officer, told Capitol News Illinois last month that her office has “been telling dispensaries, as they have been asking us” they can now sell craft-grown products to medical patients.“There was just a track and trace issue on our end, but never anything statutorily,” she said.
Dilpreet Raju
/
Capitol News IllinoisThe graphic shows how cannabis grown in Illinois gets from cultivation centers to customers.
No notice has been posted, but Johnson’s verbal guidance comes almost two years after the first craft grow business went online in Illinois.It allows roughly 150,000 medical patients, who dispensary owners say are the most consistent purchasers of marijuana, to buy products made by social equity businesses without paying recreational taxes. However — even as more dispensaries open — the number available to medical patients has not increased since 2018, something the Cannabis Regulation Oversight Office “desperately” wants to see changed. Johnson said Illinois is a limited license state, meaning “there are caps on everything” to help control the relatively new market.Berwyn Thompkins, who operates two cannabis businesses, said the rules limited options for patients and small businesses.“It’s about access,” Thompkins said. “Why wouldn’t we want all the patients — which the (adult-use) program was initially built around — why wouldn’t we want them to have access? They should have access to any dispensary.”Customers with a medical marijuana card pay a 1% tax on all marijuana products, whereas recreational customers pay retail taxes between roughly 20 and 40% on a given cannabis product, when accounting for local taxes.While Illinois has received praise for its equity-focused cannabis law, including through an independent study that showed more people of color own cannabis licenses than in any other state, some industry operators say they’ve experienced many unnecessary hurdles getting their businesses up and running.The state, in fact, announced last month that it had opened its 100th social equity dispensary.But Steve Olson, purchasing manager at a pair of dispensaries (including one dual-purpose dispensary) near Rockford, said small specialty license holders have been left in the lurch since the first craft grower opened in October 2022.“You would think that this would be something they’re (the government) trying to help out these social equity companies with, but they’re putting handcuffs on them in so many different spots,” he said. “One of them being this medical thing.”Olson said he contacted state agencies, including the Department of Financial and Professional Regulation, months ago about whether craft products can be sold to medical patients at their retail tax rate, but only heard one response: “They all say it was an oversight.”This potentially hurt social equity companies because they sell wholesale to dispensaries and may have been missing out on a consistent customer base through those medical dispensaries.Olson said the state’s attempts to provide licensees with a path to a successful business over the years, such as with corrective lotteries that granted more social equity licenses, have come up short.“It’s like they almost set up the social equity thing to fail so the big guys could come in and swoop up all these licenses,” Olson said. “I hate to feel like that but, if you look at it, it’s pretty black and white.”Olson said craft companies benefit from any type of retail sale.“If we sell it to medical patients or not, it’s a matter of, ‘Are we collecting the proper taxes?’ That’s all it is,” he said.State revenue from cannabis taxes, licensing costs and other fees goes into the Cannabis Regulation Fund, which is used to fund a host of programs, including cannabis offense expungement, the general revenue fund, and the R3 campaign aiming to uplift disinvested communities.For fiscal year 2024, nearly $256 million was paid out from Cannabis Regulation Fund for related initiatives, which includes almost $89 million transferred to the state’s general revenue fund and more than $20 million distributed to local governments, according to the Illinois Department of Revenue.Medical access still limitedThe state’s 55 medical dispensaries that predate the 2020 legalization law, mostly owned by publicly traded multistate operators that had been operating in Illinois since 2014 under the state’s medical marijuana program, were automatically granted a right to licenses to sell recreationally in January 2020. That gave them a dual-purpose license that no new entrants into the market can receive under current law.Since expanding their clientele in 2020, Illinois dispensaries have sold more than $6 billion worth of cannabis products through recreational transactions alone.Nearly two-thirds of dispensaries licensed to sell to medical patients are in the northeast counties of Cook, DuPage, Kane, Lake and Will. Dual-purpose dispensaries only represent about 20 percent of the state’s dispensaries.While the state began offering recreational dispensary licenses since the adult-use legalization law passed, it has not granted a new medical dispensary license since 2018. That has allowed the established players to continue to corner the market on the state’s nearly 150,000 medical marijuana patients.But social equity licensees and advocates say there are more ways to level the playing field, including expanding access to medical sales.Johnson, who became the state’s top cannabis regulator in late 2022, expressed hope for movement during the fall veto session on House Bill 2911, which would expand medical access to all Illinois dispensaries.“We would like every single dispensary in Illinois to be able to serve medical patients,” Johnson said. “It’s something that medical patients have been asking for, for years.”Johnson said the bill would benefit patients and small businesses.“It’s something we desperately want to happen as a state system, because we want to make sure that medical patients are able to easily access what they need,” she said. “We also think it’s good for our social equity dispensaries, as they’re opening, to be able to serve medical patients.”Rep. Bob Morgan, D-Deerfield, who was the first statewide project coordinator for Illinois’ medical cannabis program prior to joining the legislature, wrote in an email to Capitol News Illinois that the state needs to be doing more for its patients.“Illinois is failing the state’s 150,000 medical cannabis patients with debilitating conditions. Too many are still denied the patient protections they deserve, including access to their medicine,” Morgan wrote, adding he would continue to work with stakeholders on further legislation.Capitol News Illinois is a nonprofit, nonpartisan news service covering state government. It is distributed to hundreds of newspapers, radio and TV stations statewide. It is funded primarily by the Illinois Press Foundation and the Robert R. McCormick Foundation, along with major contributions from the Illinois Broadcasters Foundation and Southern Illinois Editorial Association.
[ad_2]
Source link
-

 Politics2 years ago
Politics2 years agoPrenzler ‘reconsidered’ campaign donors, accepts vendor funds
-
Board Bills1 year ago
2024-2025 Board Bill 80 — Prohibiting Street Takeovers
-

 Business3 years ago
Business3 years agoFields Foods to open new grocery in Pagedale in March
-

 Board Bills3 years ago
Board Bills3 years ago2022-2023 Board Bill 168 — City’s Capital Fund
-

 Business3 years ago
Business3 years agoWe Live Here Auténtico! | The Hispanic Chamber | Community and Connection Central
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoOK, That New Cardinals/Nelly City Connect Collab Is Kind of Great
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoSt.Louis Man Sounds Just Like Whitley Hewsten, Plans on Performing At The Shayfitz Arena.
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoSt. Louis’ New Museum of Illusions Is Ready to Book Your Visit